What you should know about your motorbike’s suspension
You are a motorbike enthusiast, a professional rider or own a sports bike, there are few basic concepts you should know about your bike’s suspension.
Role of suspension in your bike is to absorb the road disturbances from transmitting to the bike’s chassis & rider. Another important role of your bike’s suspension is to keep the tires in contact with the road surface & provide the required road adhesion/grip. The suspension also provides the stability to the bike by maintaining the required geometry at high speeds. The suspension also plays a critical role in the overall handling behavior of the bike during turning, cornering & braking.
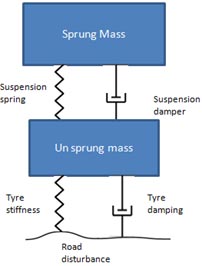
Basic tire suspension model is governed by principles of mechanical vibration. Tire is a form of spring which deflects under load & absorbs the bumps before it reaches the unsprung portion of your bike. The suspension of your bike is tuned in accordance with tire stiffness hence you should be careful when you install different specification tire on your bike & consider re-tuning of suspension. The tire also damps the energy absorbed but this is very minimal as compared to the suspension damping. Unsprung mass includes the bike’s components below the suspension springs which include wheels, tires & other brake parts mounted on a wheel. The lower unsprung mass as compared to sprung mass helps in achieving better ride comfort & road adhesion. Sprung mass comprises of the bike’s chassis, the rider as well as all parts of bike which are present above the suspension. The suspension comprises of a spring & a damper. The function of spring is to compress under loads coming from road disturbances. However, the spring releases its energy by springing back to its original position & takes a long time to settle in absence of a damper working with it. The role of the damper is to reduce the spring movement & settle the spring early so that rider does not feel the bouncing movement. The damper basically converts the kinetic energy of spring movement into heat due to the fluid movement inside the damper & hence dampens the vibrations. The damper science is complex & beyond scope of this article.
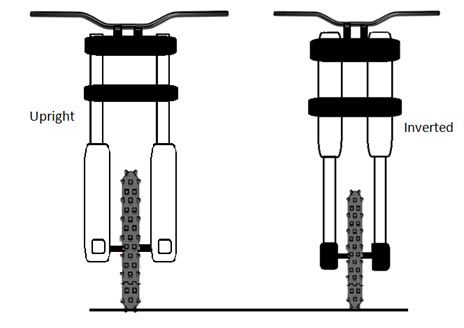
Types of suspension can be divided into front & rear suspension. Front suspension external construction can be either a telescopic upright type OR Inverted (upside down) type. Inverted type front fork has higher rigidity & delivers superior handling performance. Hence you can see inverted front suspension on performance bikes. Inverted front fork also facilitates in achieving lower unsprung mass which is beneficial in achieving enhanced ride comfort & road grip.
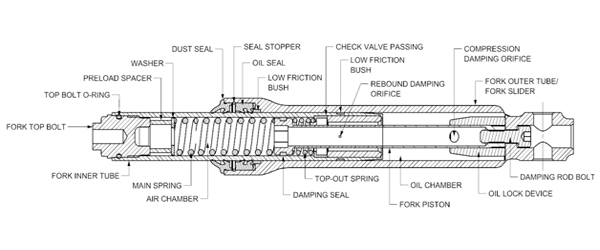
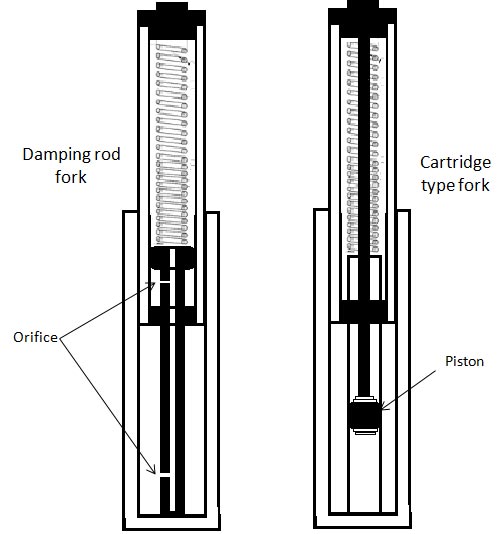
Internal construction of front suspension can be either damping rod type or cartridge type. Orifice type construction is more common with commuter bikes owing to its lesser cost & simpler construction. Cartridge type offers better damping characteristics than damping rod type fork being a piston controlled oil flow. Cartridge type front forks hence offer enhanced ride comfort.
Rear suspension layout geometry can be twin shock and mono shock type. Twin shock geometry is more common with commuter bikes whereas mono shock geometry has become standard with performance motorcycles be it high speed racing or off road motocross. Monoshock geometry offers higher cornering stability, eliminates the twisting torque on swingarm and offers longer wheel travel. The overall handling performance is superior with mono shock as compared to twin shock.

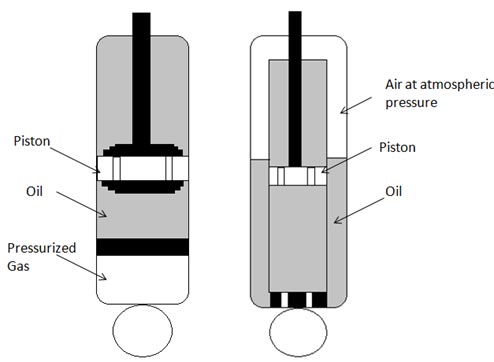
The internal construction of rear suspension can be either twin tube or monotube type. Monotube type shock absorber facilitates adopting higher size piston for better damping stability & also offers better heat dissipation. Twin tube construction is simpler to manufacture & present on majority of entry level commuting bikes. Another category in rear suspension is pure hydraulic or gas charged. Pure hydraulic type depends completely on inherent response of oil to generate the damping however gas charged type rear suspension uses inert gas at pressure to reduce the damping response time of oil & hence offers better damping response. This improvement in damping response becomes very useful to achieve the stability during high speed cornering & also offers enhanced ride comfort.